notepadpp-multireplace
MultiReplace for Notepad++
MultiReplace is a Notepad++ plugin that allows users to create, store, and manage search and replace strings within a list, perfect for use across different sessions or projects. It increases efficiency by enabling multiple replacements at once, supports sorting and applying operations to specific columns in CSV files, and offers flexible options for replacing text in various ways.
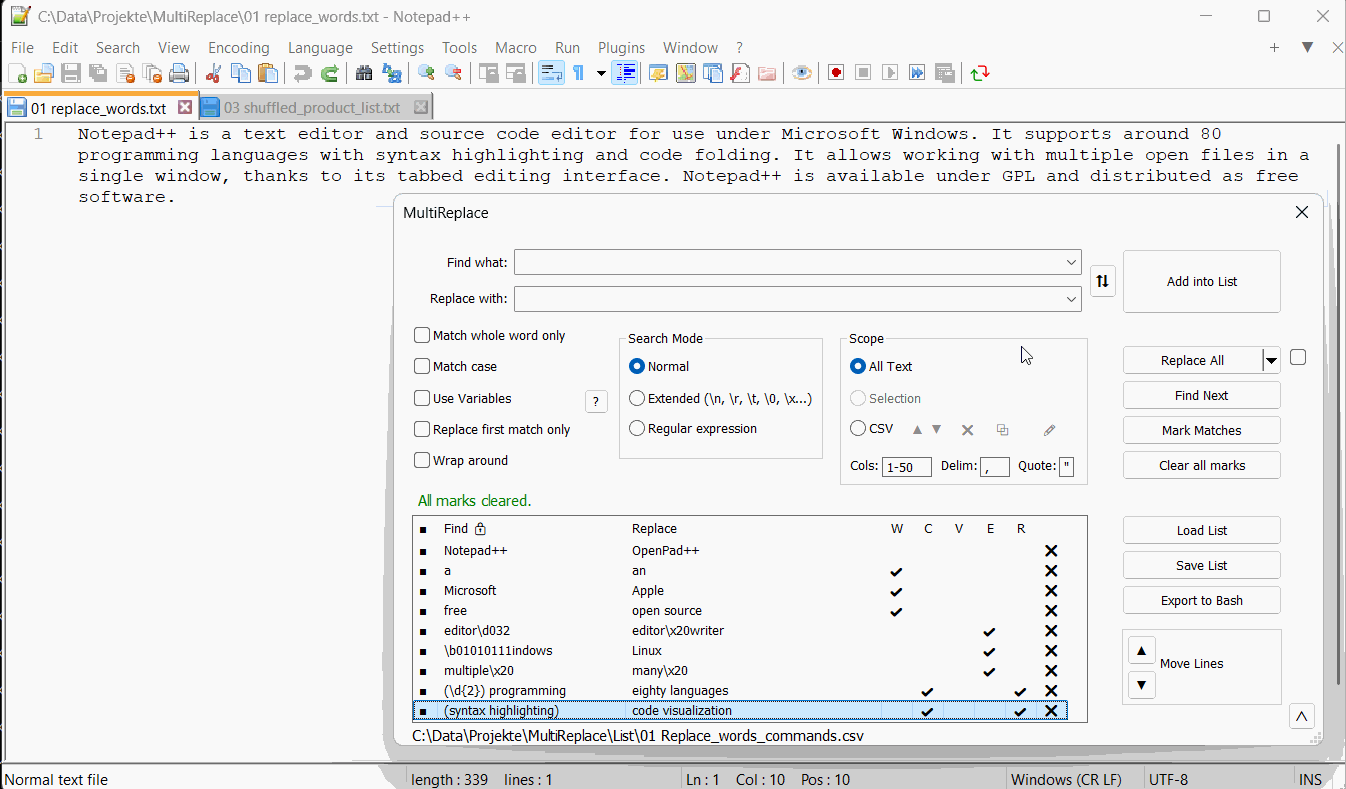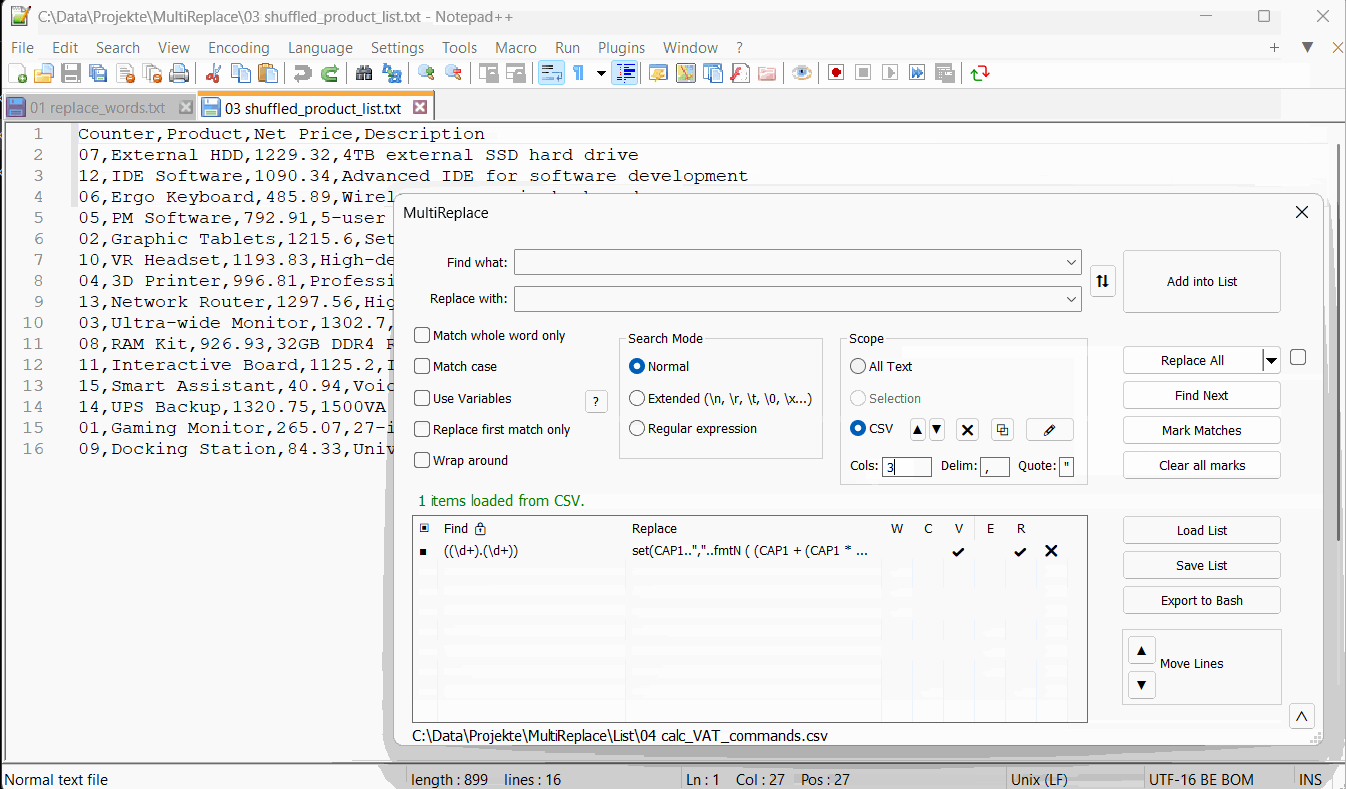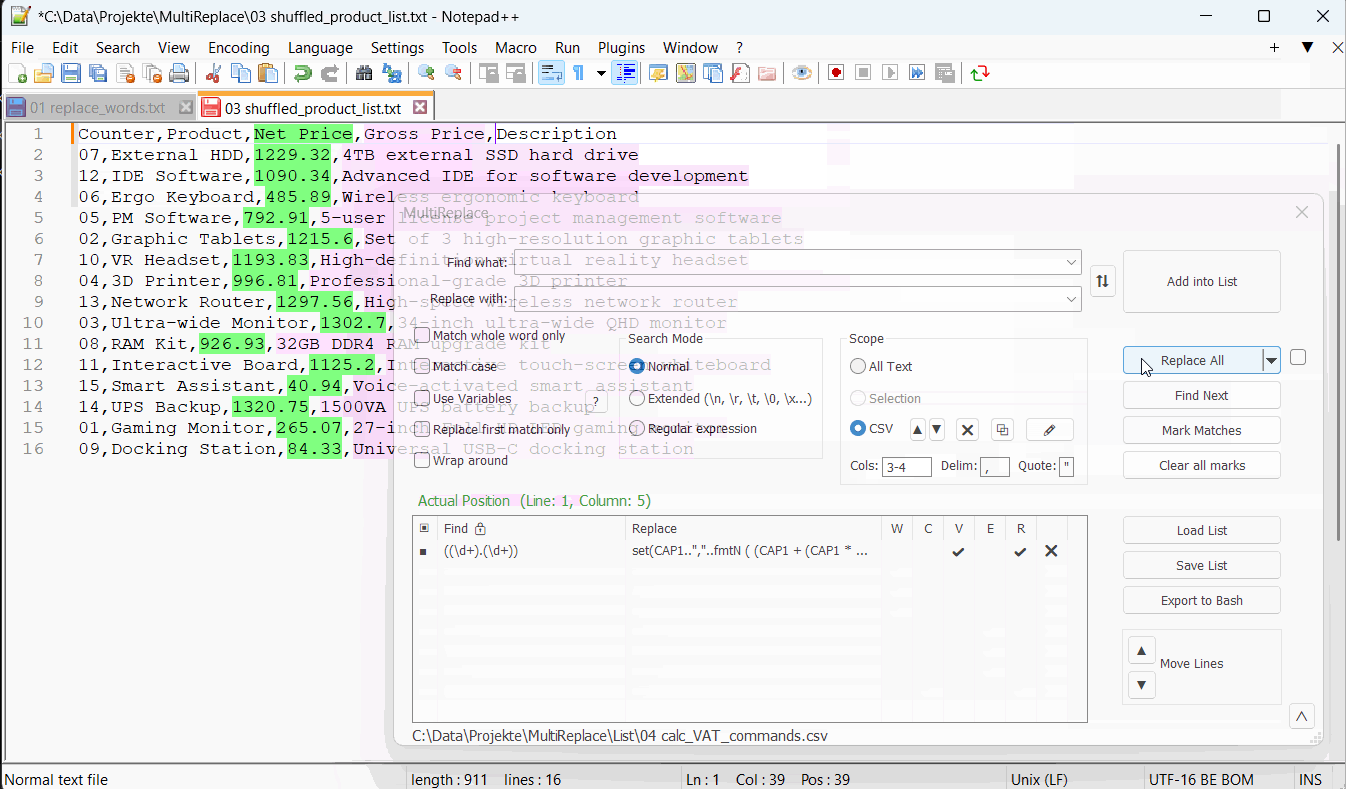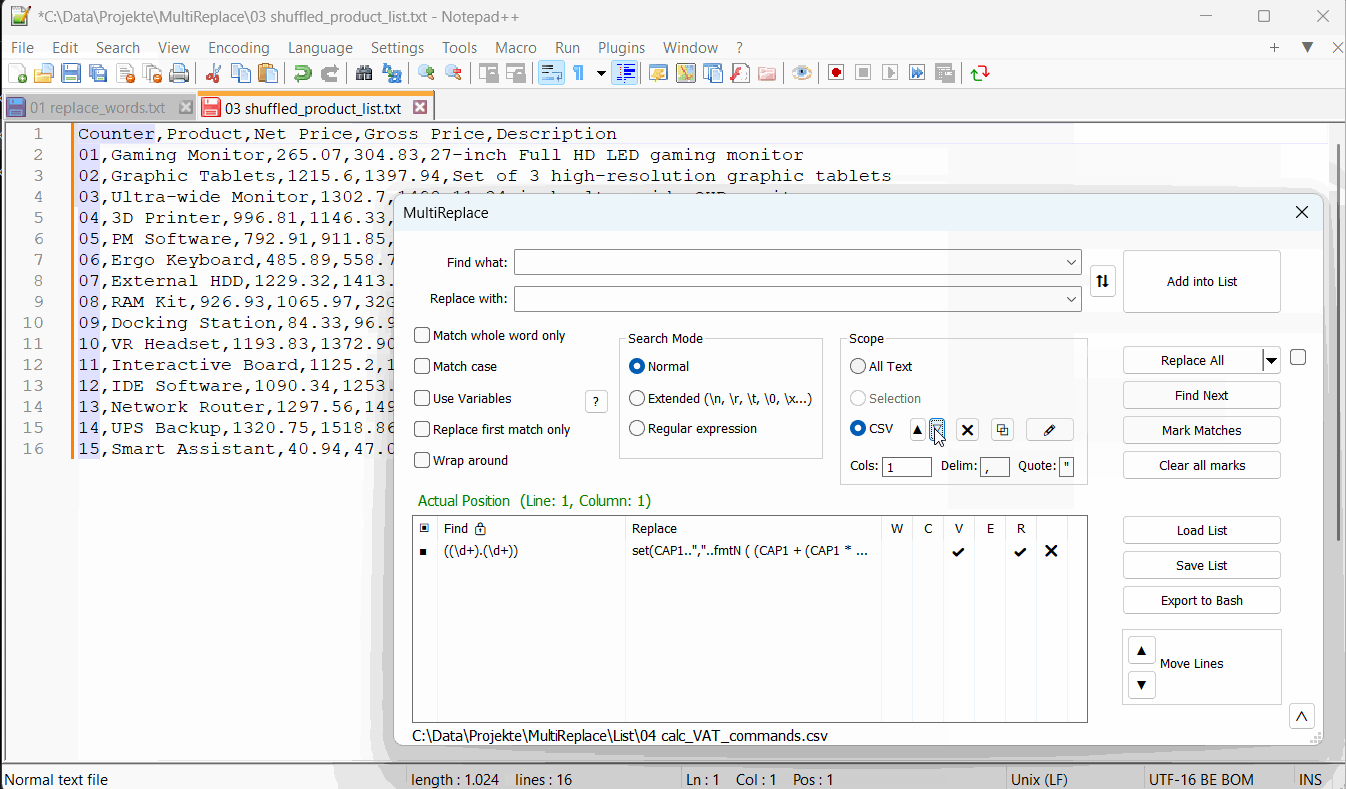
Table of Contents
- Key Features
- Match and Replace Options
- Scope Functions
- CSV Processing Functions
- Option ‘Use Variables’
- User Interaction and List Management
- Data Handling
- UI and Behavior Settings
Key Features
- Multiple Replacements: Perform multiple replacements in a single operation, in one document or across all open documents
- Save and Load Lists: Store and load search/replace lists for reuse across different sessions or projects, including all relevant settings.
- Selection Support: Supports rectangular and multiple selections for targeted replacements.
- CSV Column Operations: Search, replace, sort, or highlight specific columns in CSV or other delimited files by selecting column numbers.
- Conditional Replacements: Use variables, conditions, and mathematical operations for complex replacements, fully integrated into the replacement list like regular entries.
- Highlight Matches: Mark multiple search terms in the text, each with a distinct color for easy differentiation.
- Bash Script Export: Export replacement operations as a bash script for use outside of Notepad++.
Match and Replace Options
Match Whole Word Only: When this option is enabled, the search term is matched only if it appears as a whole word. This is particularly useful for avoiding partial matches within larger words, ensuring more precise and targeted search results.
Match Case: Selecting this option makes the search case-sensitive, meaning ‘Hello’ and ‘hello’ will be treated as distinct terms. It’s useful for scenarios where the case of the letters is crucial to the search.
Use Variables: This feature allows the use of variables within the replacement string for dynamic and conditional replacements. For more detailed information, refer to the Option ‘Use Variables’ chapter.
Replace First Match Only: For Replace-All operations, this option replaces only the first occurrence of a match for each entry in a Search and Replace list, instead of all matches in the text. This is useful when using different replace strings with the same find pattern. The same effect can be achieved with the ‘Use Variables’ option using cond(CNT == 1, 'Replace String') for conditional replacements.
Wrap Around: When this option is active, the search will continue from the beginning of the document after reaching the end, ensuring that no potential matches are missed in the document.
Scope Functions
Scope functions define the range for searching and replacing strings:
- Selection Option: Supports Rectangular and Multiselect to focus on specific areas for search or replace.
- CSV Option: Enables targeted search or replacement within specified columns of a delimited file.
Cols: Specify the columns for focused operations.Delim: Define the delimiter character.Quote: Delineate areas where characters are not recognized as delimiters.
CSV Processing Functions
Sorting, Deleting, and Copying
- Sorting Lines in CSV by Columns: Ascend or descend, combining columns in any prioritized order.
- Toggle Sort: Allows users to return columns to their initial unsorted state with just an extra click on the sorting button. This feature is effective even after rows are modified, deleted, or added.
- Exclude Header Lines from Sorting: When sorting CSV files with the CSV scope selected, you can exclude a specified number of top lines (usually header rows) from sorting. Configure this behavior using the
HeaderLinesparameter in the INI file. For details, see theINI File Settings. - Deleting Multiple Columns: Remove multiple columns at once, cleaning obsolete delimiters.
- Clipboard Column Copying: Copy columns with original delimiters to clipboard.
Numeric Sorting in CSV
For accurate numeric sorting in CSV files, the following settings and regex patterns can be used:
| Purpose | Find Pattern | Replace With | Regex | Use Variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Align Numbers with Leading Zeros (Decimal) | \b(\d*)\.(\d{2}) |
set(string.rep("0",9-string.len(string.format("%.2f", CAP1)))..string.format("%.2f", CAP1)) |
Yes | Yes |
| Align Numbers with Leading Zeros (Non-decimal) | \b(\d+) |
set(string.rep("0",9-string.len(CAP1))..CAP1) |
Yes | Yes |
| Remove Leading Zeros (Decimal) | \b0+(\d*\.\d+) |
$1 |
Yes | No |
| Remove Leading Zeros (Non-decimal) | \b0+(\d*) |
$1 |
Yes | No |
Option ‘Use Variables’
Activate the ‘Use Variables’ checkbox to employ variables associated with specified strings, allowing for conditional and computational operations within the replacement string. This Dynamic Substitution is compatible with all search settings of Search Mode, Scope, and the other options. This functionality relies on the Lua engine.
Note: Utilize either the set() or cond() command in ‘Replace with:’ to channel the output as the replacement string. Only one of these commands should be used at a time.
Variables Overview
| Variable | Description |
|———-|————-|
| CNT | Count of the detected string. |
| LINE | Line number where the string is found. |
| APOS | Absolute character position in the document. |
| LPOS | Relative line position. |
| LCNT | Count of the detected string within the line. |
| COL | Column number where the string was found (CSV-Scope option selected).|
| MATCH| Contains the text of the detected string, in contrast to CAP variables which correspond to capture groups in regex patterns. |
| FNAME| Filename or window title for new, unsaved files. |
| FPATH| Full path including the filename, or empty for new, unsaved files. |
| CAP1, CAP2, … | These variables are equivalents to regex capture groups, designed for use in the ‘Use Variables’ environment. They are specifically suited for calculations and conditional operations within this environment. Although their counterparts ($1, $2, …) cannot be used here.|
Decimal Separator
When MATCH and CAP variables are used to read numerical values for further calculations, both dot (.) and comma (,) can serve as decimal separators. However, these variables do not support the use of thousands separators.
Command Overview
String Composition
.. is employed for concatenation.
E.g., "Detected "..CNT.." times."
set(strOrCalc)
Directly outputs strings or numbers, replacing the matched text in the Replace String with the specified or calculated value.
| Example | Result (assuming LINE = 5, CNT = 3) |
|---|---|
set("replaceString"..CNT) |
“replaceString3” |
set(LINE+5) |
“10” |
cond(condition, trueVal, [falseVal])
Implements if-then-else logic, or if-then if falseVal is omitted. Evates the condition and pushes the corresponding value (trueVal or falseVal) to the Replace String.
| Example | Result (assuming LINE = 5) |
|---|---|
cond(LINE<=5 or LINE>=9, "edge", "center") |
“edge” |
cond(LINE<3, "Modify this line") |
(Original text remains unchanged) |
cond(LINE<10, cond(LINE<5, cond(LINE>2, "3-4", "0-2"), "5-9"), "10+") |
“5-9” (Nested condition) |
init({Variable1=Value1, Variable2=Value2, …})
Initializes custom variables for use in various commands, extending beyond standard variables like CNT, MATCH, CAP1. These variables can carry the status of previous find-and-replace operations to subsequent ones.
Custom variables maintain their values throughout a single Replace-All or within the list of multiple Replace operations. So they can transfer values from one list entry to the following ones. They reset at the start of each new document in ‘Replace All in All Open Documents’.
Note: An empty Find string can be used to set variables for the entire Find and Replace list without linking it to a specific Find action. This string will not match any text but is triggered at the start of ‘Replace’ or ‘Replace All’ process when ‘Use List’ is enabled, allowing the Replace field to initialize commands like init() for the entire operation. The position of the entry in the list is irrelevant.
| Find: | Replace: | Before | After |
|---|---|---|---|
(\d+) |
init({COL2=0,COL4=0}); cond(LCNT==4, COL2+COL4); if COL==2 then COL2=CAP1 end; if COL==4 then COL4=CAP1 end; |
1,20,text,2,02,30,text,3,03,40,text,4,0 |
1,20,text,2,22.02,30,text,3,33.03,40,text,4,44.0 |
\d{2}-[A-Z]{3} |
init({MATCH_PREV=''}); cond(LCNT==1,'Moved', MATCH_PREV); MATCH_PREV=MATCH; |
12-POV,00-PLC65-SUB,00-PLC43-VOL,00-PLC |
Moved,12-POVMoved,65-SUBMoved,43-VOL |
fmtN(num, maxDecimals, fixedDecimals)
Formats numbers based on precision (maxDecimals) and whether the number of decimals is fixed (fixedDecimals being true or false).
Note: The fmtN command can exclusively be used within the set and cond commands.
| Example | Result |
|————————————-|———|
| set(fmtN(5.73652, 2, true)) | “5.74” |
| set(fmtN(5.0, 2, true)) | “5.00” |
| set(fmtN(5.73652, 4, false)) | “5.7365”|
| set(fmtN(5.0, 4, false)) | “5” |
Operators
| Type | Operators |
|————-|——————————-|
| Arithmetic | +, -, *, /, ^, % |
| Relational | ==, ~=, <, >, <=, >=|
| Logical | and, or, not |
If-Then Logic
If-then logic is integral for dynamic replacements, allowing users to set custom variables based on specific conditions. This enhances the versatility of find-and-replace operations.
Note: Do not embed cond(), set(), or init() within if statements; if statements are exclusively for adjusting custom variables.
Syntax Combinations
if condition then ... endif condition then ... else ... endif condition then ... elseif another_condition then ... endif condition then ... elseif another_condition then ... else ... end
Example
This example shows how to use if statements with cond() to manage variables based on conditions:
init({MVAR=""}); if CAP2~=nil then MVAR=MVAR..CAP2 end; cond(string.sub(CAP1,1,1)~="#", MVAR); if CAP2~=nil then MVAR=string.sub(CAP1,4,-1) end
DEBUG option
The DEBUG option lets you inspect global variables during replacements. When enabled, it opens a message box displaying the current values of all global variables for each replacement hit, requiring confirmation to proceed to the next match. Initialize the DEBUG option in your replacement string to enable it.
| Find: | Replace with: |
|---|---|
(\d+) |
init({DEBUG=true}); set("Number: "..CAP1) |
More Examples
| Find in: | Replace with: | Description/Expected Output | Regex | Scope CSV |
|———————|——————————————————————————-|—————————————————————————————————————-|——-|———–|
| ; | cond(LCNT==5,";Column5;") | Adds a 5th Column for each line into a ; delimited file. | No | No |
| key | set("key"..CNT) | Enumerates key values by appending the count of detected strings. E.g., key1, key2, key3, etc. | No | No |
| (\d+) | set(CAP1.."€ The VAT is: ".. (CAP1 * 0.15).."€ Total with VAT: ".. (CAP1 + (CAP1 * 0.15)).."€") | Finds a number and calculates the VAT at 15%, then displays the original amount, the VAT, and the total amount. E.g., 50 becomes 50€ The VAT is: 7.5€ Total with VAT: 57.5€ | Yes | No |
| --- | cond(COL==1 and LINE<3, "0-2", cond(COL==2 and LINE>2 and LINE<5, "3-4", cond(COL==3 and LINE>=5 and LINE<10, "5-9", cond(COL==4 and LINE>=10, "10+")))) | Replaces --- with a specific range based on the COL and LINE values. E.g., 3-4 in column 2 of lines 3-4, and 5-9 in column 3 of lines 5-9 assuming --- is found in all lines and columns.| No | Yes |
| (\d+)\.(\d+)\.(\d+)| cond(CAP1 > 0 and CAP2 == 0 and CAP3 == 0, MATCH, cond(CAP2 > 0 and CAP3 == 0, " " .. MATCH, " " .. MATCH)) | Alters the spacing based on the hierarchy of the version numbers, aligning lower hierarchies with spaces as needed. E.g., 1.0.0 remains 1.0.0, 1.2.0 becomes ` 1.2.0, indicating a second-level version change.| Yes | No |
| (\d+) | set(CAP1 * 2) | Doubles the matched number. E.g., 100 becomes 200. | Yes | No |
| ; | cond(LCNT == 1, string.rep(“ “, 20- (LPOS))..”;”) | Inserts spaces before the semicolon to align it to the 20th character position if it's the first occurrence. | No | No |
| - | cond(LINE == math.floor(10.5 + 6.25 * math.sin((2 * math.pi * LPOS) / 50)), “”, “ “) | Draws a sine wave across a canvas of '-' characters spanning at least 20 lines and 80 characters per line. | No | No |
| ^(.)$ | init({MATCH_PREV=1}); cond(MATCH == MATCH_PREV, ‘’); MATCH_PREV=MATCH; | Removes duplicate lines, keeping the first occurrence of each line. Matches an entire line and uses MATCH_PREV` to identify and remove consecutive duplicates. | Yes | No |
Engine Overview
MultiReplace uses the Lua engine, allowing for Lua math operations and string methods. Refer to Lua String Manipulation and Lua Mathematical Functions for more information.
User Interaction and List Management
Manage search and replace strings within the list using the context menu, which provides comprehensive functionalities accessible by right-clicking on an entry, using direct keyboard shortcuts, or mouse interactions. Here are the detailed actions available:
Context Menu and Keyboard Shortcuts
Right-click on any entry in the list or use the corresponding keyboard shortcuts to access these options:
| Menu Item | Shortcut | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Transfer to Input Fields | Alt+Up | Transfers the selected entry to the input fields for editing. |
| Search in List | Ctrl+F | Initiates a search within the list entries. Inputs are entered in the “Find what” and “Replace with” fields. |
| Cut | Ctrl+X | Cuts the selected entry to the clipboard. |
| Copy | Ctrl+C | Copies the selected entry to the clipboard. |
| Paste | Ctrl+V | Pastes content from the clipboard into the list. |
| Edit Field | Opens the selected entry for direct editing. | |
| Delete | Del | Removes the selected entry from the list. |
| Select All | Ctrl+A | Selects all entries in the list. |
| Enable | Alt+E | Enables the selected entries, making them active for operations. |
| Disable | Alt+D | Disables the selected entries to prevent them from being included in operations. |
Note on the ‘Edit Field’ option: When you paste text into the edit field opened in the list, any line breaks are automatically removed. This simplifies the process of inserting complex, structured ‘Use Variables’ statements without the need to convert them into a single line first. However, make sure to include the necessary final semicolons and spaces.
Additional Interactions:
- Space Key: Toggles the activation state of selected entries, similar to using Alt+E to enable or Alt+D to disable.
- Double-Click: Mirrors the ‘Transfer to Input Fields’ action by transferring the contents of a row with their options to the input fields, equivalent to pressing Alt+Up.
List Columns
- Find: The text or pattern to search for.
- Replace: The text or pattern to replace with.
- Options Columns:
- W: Match whole word only.
- C: Match case.
- V: Use Variables.
- N: Normal search mode.
- E: Extended search mode.
- R: Regular expression mode.
- Additional Columns:
- Find Count: Displays the number of times each ‘Find what’ string is detected.
- Replace Count: Shows the number of replacements made for each ‘Replace with’ string.
- Comments: Add custom comments to entries for annotations or additional context.
- Delete: Contains a delete button for each entry, allowing quick removal from the list.
You can manage the visibility of the additional columns via the Header Column Menu by right-clicking on the header row.
List Toggling
- “Use List” checkbox toggles operation application between all list entries or the “Find what:” and “Replace with:” fields.
Entry Interaction and Limits
- Manage Entries: Manage search and replace strings in a list, and enable or disable entries for replacement, highlighting or searching within the list.
- Highlighting: Highlight multiple find words in unique colors for better visual distinction, with over 20 distinct colors available.
- Character Limit: Field limits of 4096 characters for “Find what:” and “Replace with:” fields.
Data Handling
Import/Export
- Supports import/export of search and replace strings with their options in CSV format, including selection states.
- Allows loading list files via drag and drop into the Search and Replace list.
- Adherence to RFC 4180 standards for CSV, enabling compatibility and easy interaction with other CSV handling tools.
- Enables reuse of search and replace operations across sessions and projects.
Bash Script Export
- Exports Find and Replace strings into a runnable script, aiming to encapsulate the full functionality of the plugin in the script. However, due to differences in tooling, complete compatibility cannot be guaranteed.
- This feature intentionally does not support the value
\0in the Extended Option to avoid escalating environment tooling requirements.
UI and Behavior Settings
Column Locking
Lock column widths to prevent resizing during window adjustments. This is useful for key columns like Find, Replace, and Comments.
- How to Lock: Double-click the column divider in the header to toggle locking. A lock icon appears in the header for locked columns.
- Effect: Locked columns keep their width fixed, while unlocked ones adjust dynamically.
Configuration Settings
The MultiReplace plugin provides several configuration options, including transparency, scaling, and behavior settings, that can be adjusted via the INI file located at:
C:\Users\<Username>\AppData\Roaming\Notepad++\plugins\Config\MultiReplace.ini
INI File Settings:
- HeaderLines: Specifies the number of top lines to exclude from sorting as headers.
- Default:
HeaderLines=1(first line is excluded from sorting). - Description: Set this value to exclude a specific number of lines at the top of the file from being sorted during CSV operations. Useful for preserving header rows in CSV files.
- Note: If set to
0, no lines are excluded from sorting.
- Default:
- Transparency Settings:
ForegroundTransparency: Transparency level when in focus (0-255, default 255).BackgroundTransparency: Transparency level when not in focus (0-255, default 190).
- ScaleFactor: Controls the scaling of the plugin window and UI elements.
- Default:
ScaleFactor=1.0(normal size). - Range: 0.5 to 2.0.
- Description: Adjust this value to resize the plugin window and UI elements. A lower value shrinks the interface, while a higher value enlarges it.
- Default:
- DoubleClickEdits: Controls the behavior of double-clicking on list entries.
- Default:
DoubleClickEdits=1(enabled). - Description: When enabled (
1), double-clicking on a list entry allows direct in-place editing. When disabled (0), double-clicking transfers the entry to the input fields for editing.
- Default:
- Tooltips: Controls the display of tooltips in the UI.
- Default:
Tooltips=1(enabled). - Description: To disable tooltips, set
Tooltips=0in the INI file.
- Default:
- AlertNotFound: Controls notifications for unsuccessful searches.
- Default:
AlertNotFound=1(enabled). - Description: To disable the bell sound for unsuccessful searches, set
AlertNotFound=0in the INI file.
- Default:
Multilingual UI Support
The UI language settings for the MultiReplace plugin can be customized by adjusting the languages.ini file located in C:\Program Files\Notepad++\plugins\MultiReplace\. These adjustments will ensure that the selected language in Notepad++ is applied within the plugin.
Contributions to the languages.ini file on GitHub are welcome for future versions. Find the file here.


